Intel Q4 Earnings
Intel Corporation – Common is scheduled to report Q4 earnings on 30 Jan. Consensus estimates suggest $13.83 billion and $0.12 per share earnings.
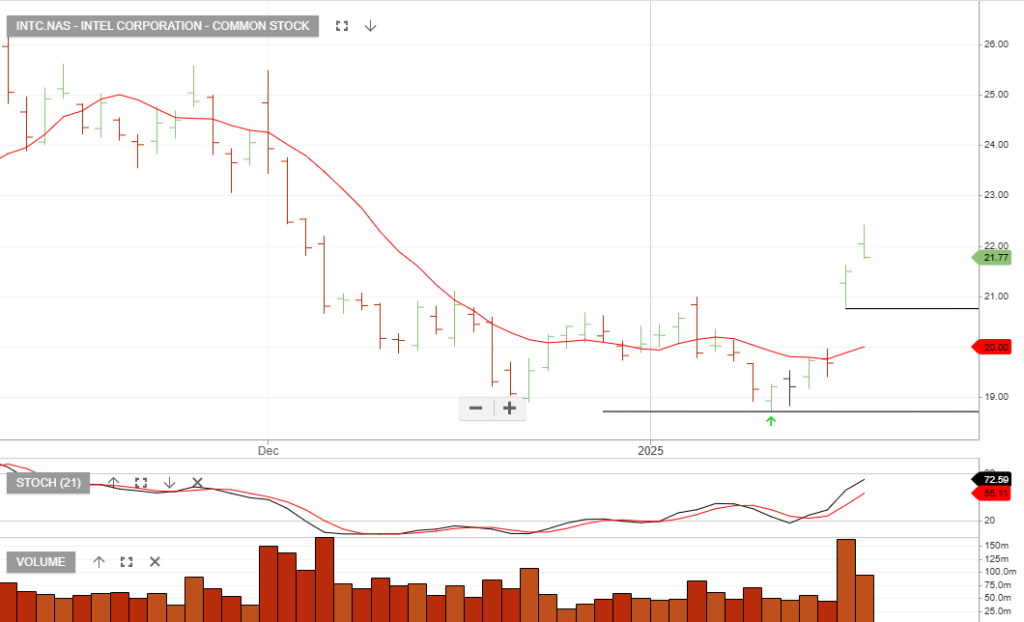
Intel Corporation – Common is scheduled to report Q4 earnings on 30 Jan. Consensus estimates suggest $13.83 billion and $0.12 per share earnings.

Intel Corporation – Common is under Algo Engine buy conditions.
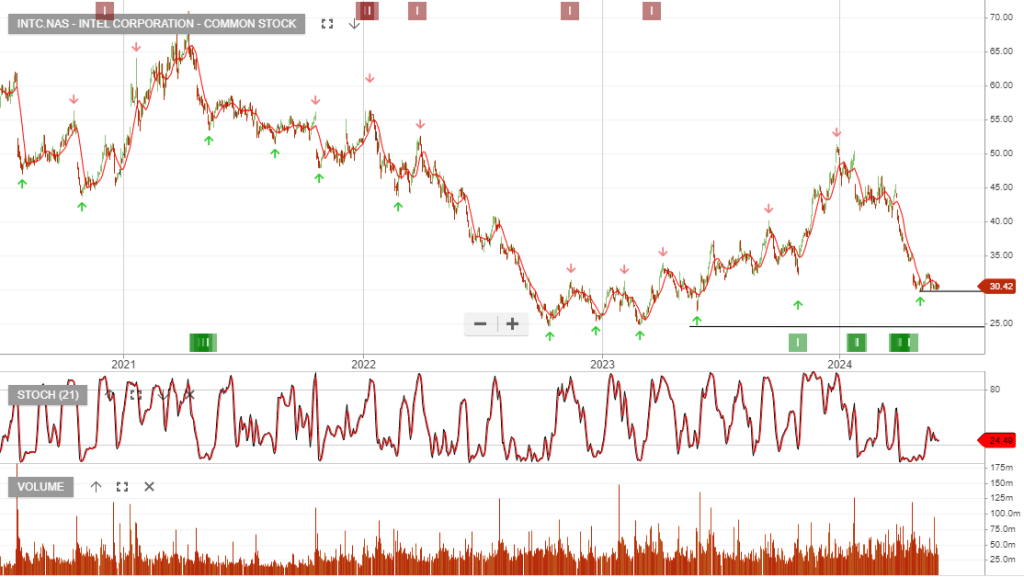
The launch of Intel’s Gaudi 3 AI accelerator and the reorganization of its foundry business are positive signs for future growth. During the first quarter, Intel’s revenues increased by 8.5% Y/Y to $12.7 billion.
The launch of Intel’s Gaudi® 3 AI accelerator in Q3, which appears to be more powerful than NVIDIA’s flagship H100 GPU, should also help the company improve the performance of its data center business, revenue to total $56 bln (+3% y/y) in 2024, and jump to $65.3 bln (+17% y/y) in 2025. Adjusted EBITDA is set to total $13.8 bln (+7% y/y) in 2024, and rocket to $20.3 bln (+47% y/y).
Effective from 1Q 2024, the company modified its segment reporting, with revenue now coming from the following business units:
1. Intel Products
2. Intel Foundry
3. All other
Client Computing Group (CCG) – this segment generates about half of the company’s revenue. It supplies central processing units for desktop PCs and notebooks.
Data Center and AI (DCAI) – The key products in this segment are CPUs, GPUs and Gaudi AI accelerators.This segment has accounted for just under 30% of the company’s total revenue in recent years
Intel Foundry – the segment that includes chip manufacturing for Intel’s own needs as well as for external customers. Intel entered the market of contract manufacturing of semiconductors in 2021 as Intel Foundry Service (IFS) to capitalize on the growing demand for foundry capacity. To provide transparency in the segment’s operations, the company in its reporting separates revenue generated from external customers and revenue from inter-segment sales within Intel. As of the end of 2023, revenue from external customers totaled $953 mln (+96% y/y), or 5% of total IFS revenue of $18.9 bln (-31% y/y).
Even though IFS revenue from external customers is relatively small, Intel has ambitious plans to expand the plants by investing its own funds and with the help of government subsidies (Under the CHIPS Act the US government has given Intel $8.5 bln in grants and the option to draw $11 bln in federal loans).
On April 25, 2024, Intel reported its Q1 FY24 earnings with revenue of $12.7 billion, a 9% increase YoY, and non-GAAP EPS of $0.18, both beating Wall Street expectations. However, the revenue guidance of $12.5 billion to $13.5 billion fell short of Wall Street’s expectation of $13.63 billion, leading to a plunge in the stock price to around $30 per share.
Intel is a high-risk recovery play in the chip space. We consider the current share price to be at an inflection point, and it will begin to rise in mid-to-late 2024. The first positive catalyst is the US government’s CHIPs Act funding payment. A multi-year recovery should follow, driven by innovation and AI data center sales.
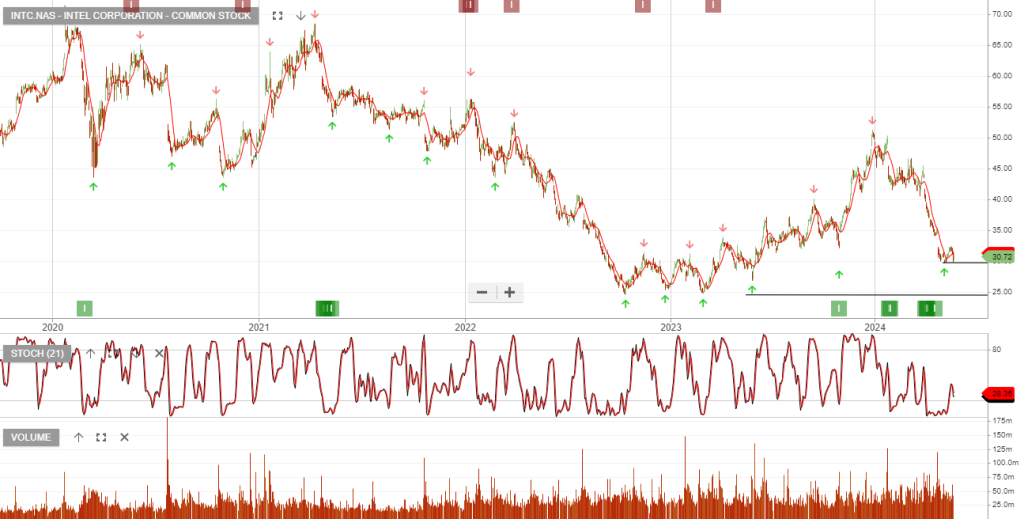
INTC:NAS The U.S. government is expected to invest $3.5B in Intel to make advanced semiconductors for military and intelligence programs. The money is part of the larger $39B Chips and Science Act grant pool aimed at boosting U.S. semiconductor manufacturing.
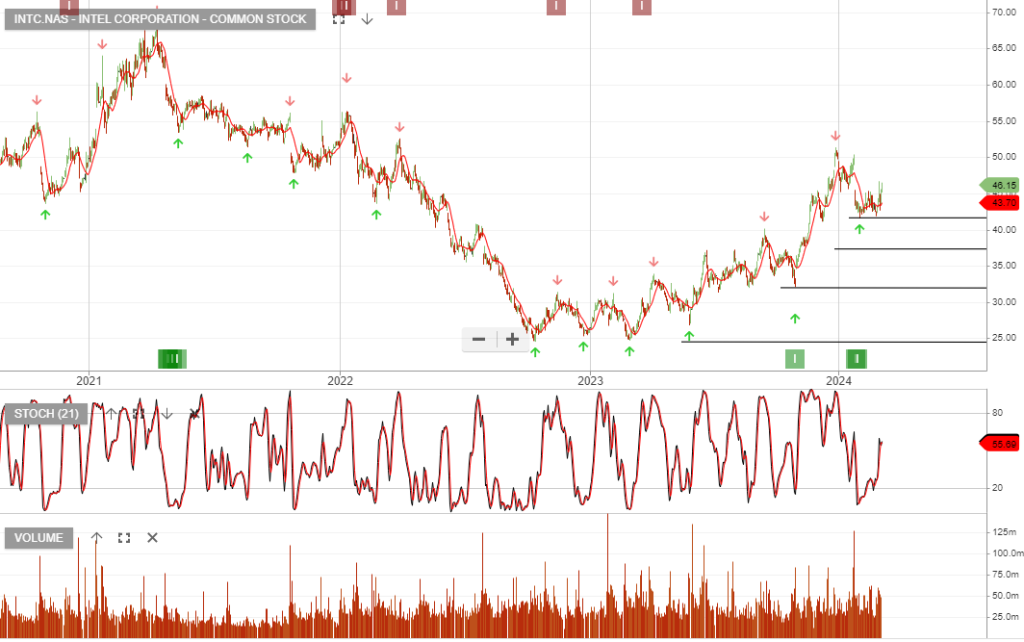
Intel Corporation – Common is a current holding in our US Trade Table, after 20 days the trade is up 22%

Intel Corporation – Common is a current holding in our US Trade Table.
Or start a free thirty day trial for our full service, which includes our ASX Research.