There are new Signals.
For our Members, please find below the latest list of signals.
For our Members, please find below the latest list of signals.
For our Members, please find below the latest list of signals.
For our Members, please find below the latest list of signals.
For our Members, please find below the latest list of signals.
For our Members, please find below the latest list of signals.
Ramsay Health Care is a buy with a stop loss at $48.72
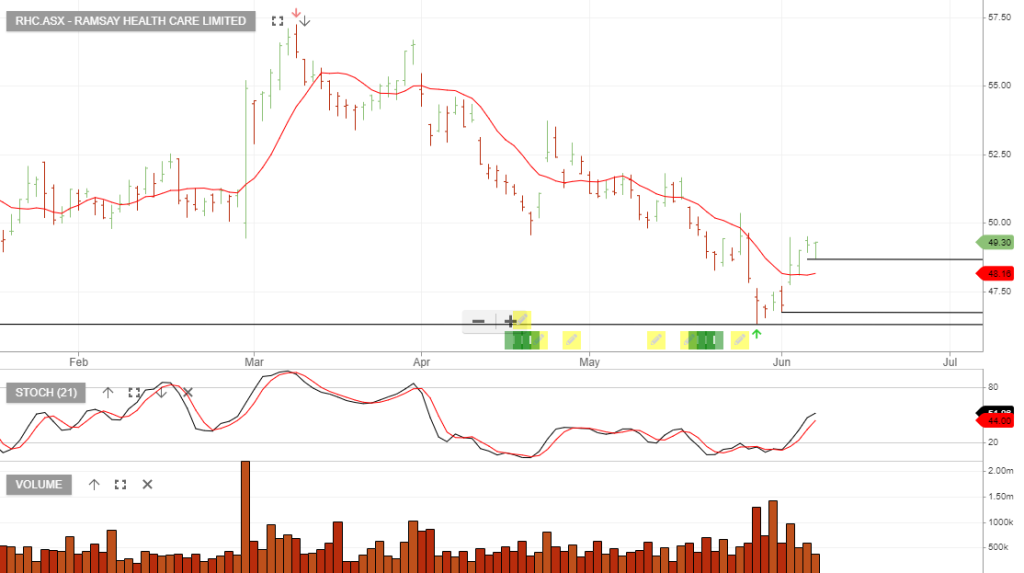
For our Members, please find below the latest list of signals.
Intel Corporation – Common is under Algo Engine buy conditions.
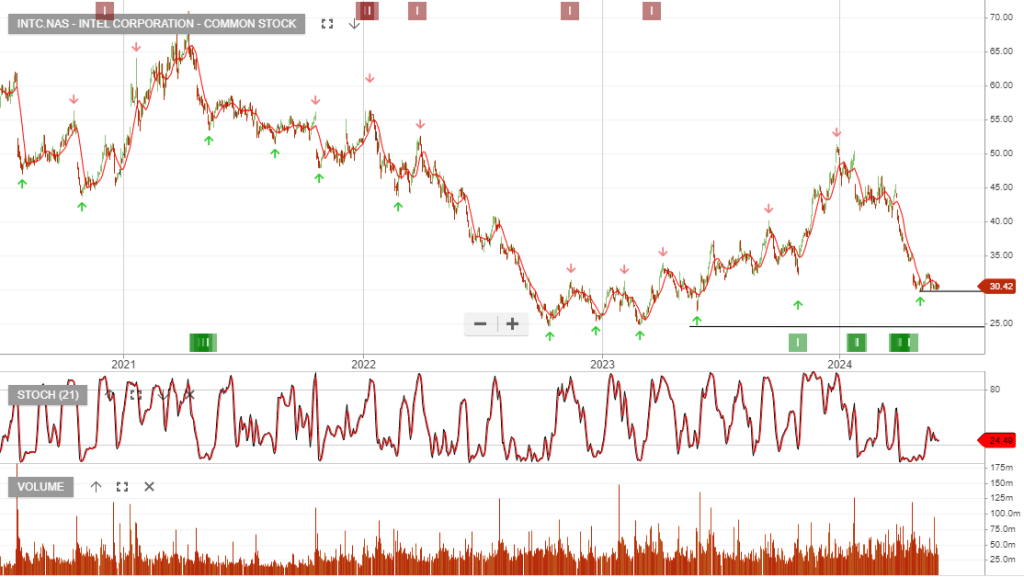
The launch of Intel’s Gaudi 3 AI accelerator and the reorganization of its foundry business are positive signs for future growth. During the first quarter, Intel’s revenues increased by 8.5% Y/Y to $12.7 billion.
The launch of Intel’s Gaudi® 3 AI accelerator in Q3, which appears to be more powerful than NVIDIA’s flagship H100 GPU, should also help the company improve the performance of its data center business, revenue to total $56 bln (+3% y/y) in 2024, and jump to $65.3 bln (+17% y/y) in 2025. Adjusted EBITDA is set to total $13.8 bln (+7% y/y) in 2024, and rocket to $20.3 bln (+47% y/y).
Effective from 1Q 2024, the company modified its segment reporting, with revenue now coming from the following business units:
1. Intel Products
2. Intel Foundry
3. All other
Client Computing Group (CCG) – this segment generates about half of the company’s revenue. It supplies central processing units for desktop PCs and notebooks.
Data Center and AI (DCAI) – The key products in this segment are CPUs, GPUs and Gaudi AI accelerators.This segment has accounted for just under 30% of the company’s total revenue in recent years
Intel Foundry – the segment that includes chip manufacturing for Intel’s own needs as well as for external customers. Intel entered the market of contract manufacturing of semiconductors in 2021 as Intel Foundry Service (IFS) to capitalize on the growing demand for foundry capacity. To provide transparency in the segment’s operations, the company in its reporting separates revenue generated from external customers and revenue from inter-segment sales within Intel. As of the end of 2023, revenue from external customers totaled $953 mln (+96% y/y), or 5% of total IFS revenue of $18.9 bln (-31% y/y).
Even though IFS revenue from external customers is relatively small, Intel has ambitious plans to expand the plants by investing its own funds and with the help of government subsidies (Under the CHIPS Act the US government has given Intel $8.5 bln in grants and the option to draw $11 bln in federal loans).
PayPal has chosen the Solana blockchain to expand its stablecoin, PayPal USD, marking its first move beyond the Ethereum ecosystem.
According to an announcement on May 28, PYUSD has been added to the Solana network, allowing users to perform transactions at a lower cost. The move seeks to expand the uses of PYUSD stablecoin as a payment method for small and daily purchases.
Solana processes up to 65,000 transactions per second at costs as low as $0.0025, significantly outpacing Ethereum’s 15 transactions per second with higher fees, which may vary from $1 to $50 during times of congestion. In other words, while a transaction on Ethereum could take a few minutes to process, the same transfer using Solana could be completed in less than a minute.
The Solana network surged as the most used blockchain for stablecoin transfers since last year. According to data from analytics platform Artemis, stablecoin transfer volume on Solana reached $1.5 trillion over the past year, largely surpassing Ethereum’s volume of $885 billion over the same period.
PayPal launched its stablecoin in August 2023 in collaboration with Paxos Trust Company. The stablecoin was initially issued only on Ethereum as an ERC-20 token and is backed by U.S. dollar deposits, short-term Treasurys, and cash equivalents.
Ansell is under Algo Engine buy conditions.
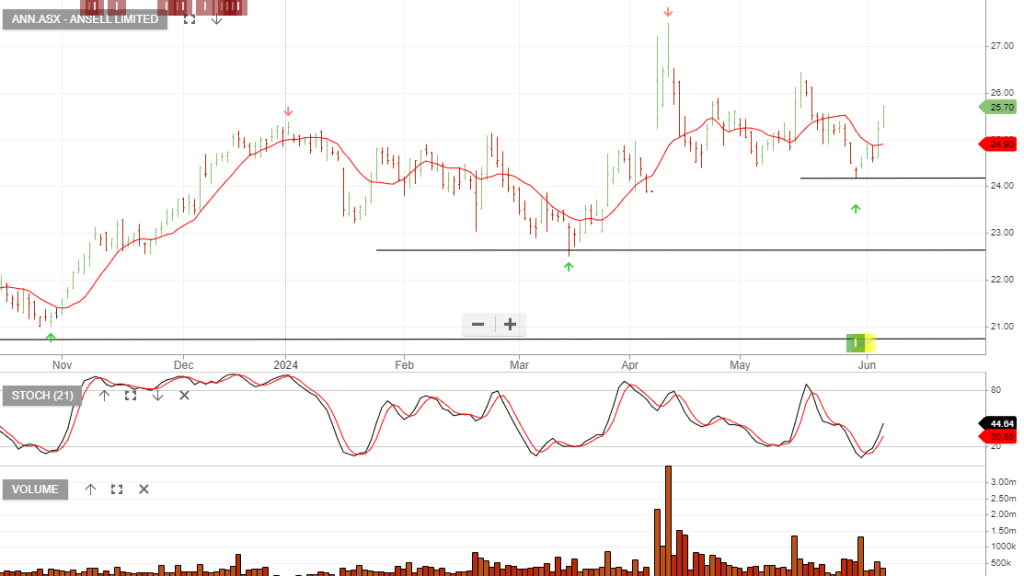
Or start a free thirty day trial for our full service, which includes our ASX Research.